EST
ENTERPRISE This is an EJBCA Enterprise feature.
Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST) is an X.509 certificate management protocol targeting public key infrastructure (PKI) clients that need to acquire client certificates and associated certificate authority (CA) certificates.
Introduction
EJBCA supports the EST protocol as defined in RFC 7030. Support for EST was added in EJBCA version 6.11.
EST provides a basic protocol for certificate enrollment and management similar to SCEP, with the following distinct advantages:
While SCEP communicates over HTTP and ensures integrity by wrapping the payload in a cryptographic envelope, EST requests are always over TLS and thus inherently secure.
EST supports ECC, while SCEP does not.
While SCEP requires a shared secret to authenticate CSRs, in EST authentication is implicit when negotiating the TLS connection.
Certificate renewal is an integral part of EST, while in SCEP it is rather an afterthought.
While not supported in EJBCA, EST supports server-side key generation, which SCEP does not.
Supported Operations
The following operations in EST are supported:
|
Name |
Description |
|
cacerts |
A GET request that returns a cert-only pkcs#7 blob containing the CA certificate (and possible chain) for the given alias that is used to issuing certificates via enrollment operation. This operation requires no authentication. |
|
simpleenroll |
A POST request with a CSR in PKCS#10 format and Base64 encoded to be signed by the specified CA for the given alias. May require an existing client certificate for authentication and/or HTTP Basic authentication via username and password. The end entity username will be set according to the specified RA name generation scheme. If there is no existing end entity with the generated username, a new end entity will be created. If an end entity with the specified username already exists, it is treated as a renewal: a new certificate is issued for the existing end entity (as long as no settings block this behavior: e.g. Enforce Unique DN or Enforce Unique Public Keys). |
|
simplereenroll |
A POST request with a CSR in PKCS#10 format and Base64 encoded to be signed by the specified CA for the given alias. Requires authenticating with the original certificate, which has to be valid (to establish a TLS connection) and not revoked. |
A request with an unsupported operation will result in an HTTP not found (404) response from the server.
EST Configuration
Access
The EJBCA EST implementation uses the Well-Known Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) definition codified in RFC 5785.
Like SCEP and CMP, EJBCA supports using EST for multiple CAs by the use of aliases. Each alias is then accessible using:
$ /.well-known/est/<alias>/<operation>When an alias with the name est is configured, this alias is available over the default EST URL, which is the URL used by the estclient, see Testing.
$ /.well-known/est/<operation>A request with an unknown alias will result in an HTTP bad request (400) response from the server.
Configuring Aliases
The following displays the EST alias configuration screen.
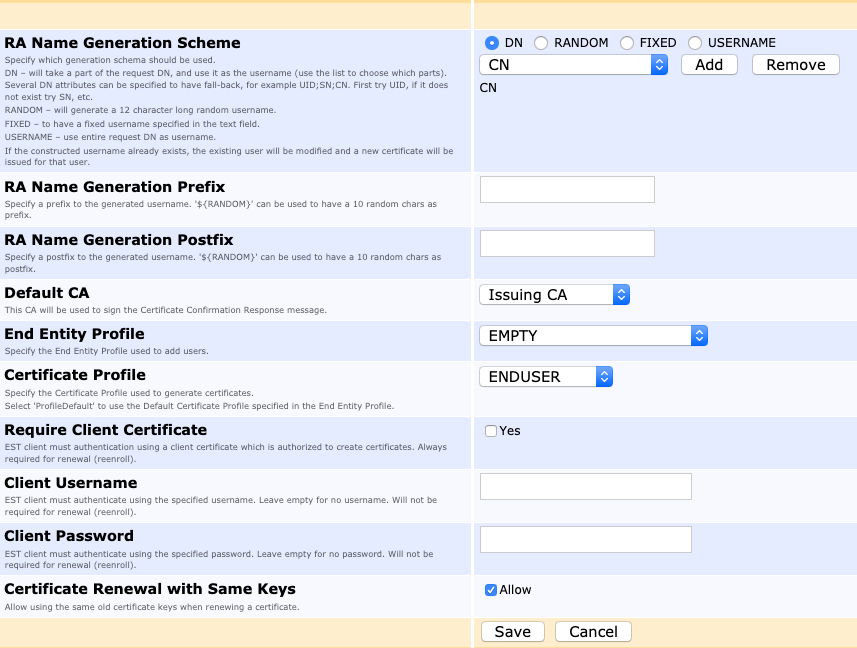
The following lists available EST alias configuration options.
|
Value |
Description |
|
RA Name Generation Scheme |
DN: Will take a part of the request DN, and use it as the username (use the list to choose which parts). Several DN attributes can be specified to have fall-back. For example: UID;SN;CN. First try UID. If it does not exist try SN, etc. |
|
RA Name Generation Prefix |
Specify a prefix to the generated username. '${RANDOM}' can be used to have a 10 random chars as prefix. |
|
RA Name Generation Postfix |
Specify a postfix to the generated username. '${RANDOM}' can be used to have a 10 random chars as postfix. |
|
RA CA Name |
The CA that this alias will issue certificate from. |
|
End Entity Profile |
The End Entity Profile that enrolling end entities will have applied to them. This defines the required DN and altName naming fields. |
|
Certificate Profile |
The Certificate Profile that enrolling end entities will have applied to them. This controls the certificate type, that is, key usage and other extensions. |
|
Require Client Certificate |
Specifies if a client certificate is required to enroll. The client certificate does not need to be known by EJBCA (if the option web.reqcertindb in conf/web.properties is set to false), but the issuing CA is. The client certificate needs to belong to a Role with full RA rights. |
|
Client username/password |
Sets a username and password to enroll. The username will be given full RA rights. If a client certificate is required, both client certificate and username/password will be checked for initial enrollment. For Renewal (re-enroll) username and password are never required, but client certificate is always required. |
|
Certificate Renewal with Same Keys |
If Allow is selected, a re-enrollment request may be performed for the same public key as before. Note that client certificate is always required for renewal, while username/password is never required, regardless of the settings above. |
Although you can configure an EST alias without client username and without requiring client certificate, such an EST alias cannot be used since either certificate or username/password authentication is required for the initial enrollment.
Configuring the Truststore
When renewing a certificate using EST, the certificate which is to be renewed is used as a client certificate to authenticate to the CA. The CA must then trust the issuer of this certificate to be able to establish a TLS connection to the PKI client. If TLS connections are handled by WildFly, you need to add the issuer chain to WildFly's truststore. If TLS connections are handled by an HTTP proxy in front of WildFly, you need to add the issuer chain to the truststore of the HTTP proxy.
WildFly
To add an issuer to WildFly's truststore, you can use keytool.
Download the CA certificate of the issuer as a PEM file, e.g. by going to CA Certificates & CRLs in EJBCA.
Transfer the CA certificate to the machine where EJBCA is installed.
Use keytool to add the CA certificate to Wildfly's truststore.
$ keytool -keystore /opt/wildfly/standalone/configuration/keystore/truststore.jks -alias <NAME_OF_CA> -importcert -file <ISSUER.PEM> -storepass changeit
Appliance
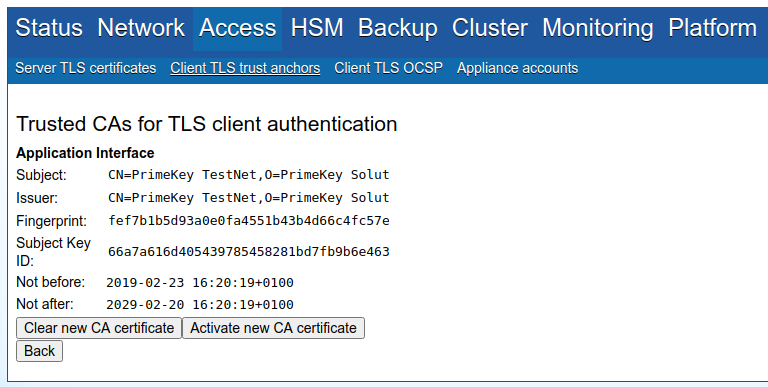
If you are using the EJBCA Hardware Appliance, you can use WebConf to modify the truststore on the appliance.
Download the CA certificate of the issuer as a PEM file, e.g. by going to CA Certificates & CRLs in EJBCA.
Go to WebConf, and click Access > Client TLS trust anchors in the menu.
In the Application interface section, click Add.
Upload the CA certificate and click Activate new CA certificate to add it to the appliance truststore.
Testing
Clone libest from Cisco and build according to instructions:
$ cd examples/client$ # via environment specify the initial CA certificate to use for verifying TLS connection.$ cp <path to server cert> server.pem$ export EST_OPENSSL_CACERT=server.pem$ # Where to save certs$ mkdir certs$ # Optionally get new CA certificates$ ./estclient -g -s <ip or hostname to EJBCA> -p 8442 -o certs --pem-output$ # certs should now contain a cacert-0-0.pem file$ # enroll with CA. publicCert.pem and privetKey.pem are the TLS client cert I wish to use for auth. RequestDN will be 'CN=myclient'$ ./estclient -e -s <ip or hostname to EJBCA> -p 8443 -o certs -c publicCert.pem -k privateKey.pem -u estadmin -h foo123 --pem-output --common-name myclient$ # certs will now contain a cert-0-0.pem and key-x-x.pem$ # client cert is about to expire, reenroll, requires client certificate authentication to the server$ ./estclient -r -s <ip or hostname to EJBCA> -p 8443 -o tmp -c tmp/cert-0-0.pem -k tmp/key-x-x.pem --pem-output$ # certs should now contain an updated cert-0-0.pem You can also test access to EST URLs using curl commands.
Here is a full work-flow example using CURL, where initial enrollment uses username/password EST authentication, and re-enroll using the existing client certificate.
# Get CA certificatescurl https://<hostname to EJBCA>:8442/.well-known/est/<name of alias>/cacerts -o cacerts.p7 --cacert ManagementCA.cacert.pem# Generate a key and CSR for a "device"# Make sure the subject DN and subject alternative name matches the end entity profile.openssl req -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout device.key -out device.csr -outform DER -subj "/CN=123456789"openssl base64 -in device.csr -out device.b64 -e# Make initial enrollment, using EST password authentication (client certificate is also possible)curl -v --cacert ManagementCA.cacert.pem --user estadmin:foo123 --data @device.b64 -o device-p7.b64 -H "Content-Type: application/pkcs10" -H "Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64" https://<hostname to EJBCA>:8442/.well-known/est/<name of alias>/simpleenroll# Convert the response into a PEM encoded certificateopenssl base64 -in device-p7.b64 -out device-p7.der -dopenssl pkcs7 -inform DER -in device-p7.der -print_certs -out device-cert.pem# Generate a new key and CSR for the device, to renew withopenssl req -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout device-new.key -out device-new.csr -outform DER -subj "/CN=123456789"openssl base64 -in device-new.csr -out device-new.b64 -e# Re-enroll by the device, authenticating with the existing key/certificatecurl -v --cacert ManagementCA.cacert.pem --key device.key --cert device-cert.pem --data @device-new.b64 -o device-new-p7.b64 -H "Content-Type: application/pkcs10" -H "Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64" https://<hostname to EJBCA>:8443/.well-known/est/<name of alias>/simplereenroll# Convert the response into a PEM encoded certificateopenssl base64 -in device-new-p7.b64 -out device-new-p7.der -dopenssl pkcs7 -inform DER -in device-new-p7.der -print_certs -out device-new-cert.pemManagementCA.cacert.pem is the Root CA certificate of the CA chain that issued the TLS server cert and needs to be configured with curl in order for the TLS connection to be established. ManagementCA is the name in a default EJBCA installation and the cert can be downloaded from the CA UI or RA UI. The examples above use port 8442 for TLS with server authentication, and port 8443 for TLS with both client and server authentication (when using a client authentication certificate and private key). The standard TLS port, 443, is used when running an Apache proxy in front or EJBCA, such as is the case with an EJBCA Enterprise Cloud instance or a PrimeKey PKI Appliance. For EJBCA Enterprise Cloud instances or the PrimeKey PKI Appliance, port 443 will work for calls with or without client certificate authentication.
You can also authenticate as EST admin using a client certificate. The command is slightly different, using certificate authentication in addition to the username/password:
# Enroll$ curl -v --cacert ManagementCA.cacert.pem --user estadmin:foo123 --cert ra-cert.pem --key ra-key.pem --data @device.b64 -o device-p7.b64 -H "Content-Type: application/pkcs10" \-H "Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64" https://<hostname to EJBCA>/.well-known/est/simpleenroll# Re-enroll$ curl -v --cacert ManagementCA.cacert.pem --key device.key --cert device-cert.pem --data @device-new.b64 -o device-new-p7.b64 -H "Content-Type: application/pkcs10" -H "Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64" https://<hostname to EJBCA>/.well-known/est/simplereenrollWorkflow Example
Example enrollment, where an RA gets CA certificate first and then gets a client certificate, using username/password authentication (the EST client acts as an RA). Next, the client performs a renewal, authenticating with the client certificate issued previously.
EST configuration is an EST alias with the name est and the following settings:
|
Setting |
Value |
|
Default CA |
EST CA |
|
End Entity Profile |
EST EE Profile (with only CN required DN attribute) |
|
Certificate Profile |
Profile Default |
|
Require Client Certificate |
false |
|
Client Username |
estadmin |
|
Client Password |
foo123 |
|
Certificate Renewal with Same Keys |
false |
Download the CA certificate of the EJBCA TLS connection (usually the default is Management CA), and set the environment variable needed for estclient:
$ export EST_OPENSSL_CACERT=/tmp/ManagementCA.cacert.pemRun the following estclient commands to generate a key and get a certificate from the CA:
$ mkdir certs# Get CA certificate, by "RA:$ ./estclient -g -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8442 -o certs --pem-output# Inspect the fetched CA certificate $ openssl x509 -in certs/cacert-0-0.pem -text -noout# Get client certificate, by "RA", authenticated with username/password$ ./estclient -e -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8442 -o certs -u estadmin -h foo123 --pem-output --common-name myclient# Inspect the fetched client certificate $ openssl x509 -in certs/cert-0-0.pem -text -noout# Re-enroll, directly by the client when certificate is about to expire, using the old client cert to authenticate with:$ ./estclient -r -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8443 -o certs -c certs/cert-0-0.pem -k certs/key-x-x.pem -u estadmin -h foo123 --pem-output# Inspect the new, renewed, client certificate $ openssl x509 -in certs/cert-0-0.pem -text -noout# Revoke the clients certificates by going to CA UI and using Search End Entities to find the end entity and revoke certificates.# Try to re-enroll again, which will not work with a revoked client certificates.$ ./estclient -r -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8443 -o certs -c certs/cert-0-0.pem -k certs/key-x-x.pem --pem-output# Enroll with an EC key. First we have to generate the key, a Prime256v1 key on this case, and then use this key for enrollment.openssl ecparam -name prime256v1 -genkey -noout -out prime256v1-key.pem./estclient -e -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8442 -o certs -u estadmin -h foo123 --pem-output --common-name myclient -x prime256v1-key.pem$ openssl x509 -in certs/cert-0-0.pem -text -noout# Re-enroll, also with EC, using the same key (using the same key can be dissalowed in the EST alias)../estclient -r -s 127.0.0.1 -p 8443 -o certs -c certs/cert-0-0.pem -k prime256v1-key.pem --pem-output -x prime256v1-key.pem$ openssl x509 -in certs/cert-0-0.pem -text -noout